Provisional translation
Innovative Strategy for Energy and the Environment
September 14, 2012
The Energy and Environment Council Government of Japan
Table of Contents
Introduction.......................................................................................... 1
1. Realization of a Society Not Dependent on Nuclear Power in Earliest Possible Future
............................................................................................................ 4
2. Realization of Green Energy Revolution .......................................... 10
(1) Electricity saving and energy saving ............................................... 10
(2) Renewable energy......................................................................... 13
3. For Ensuring Stable Supply of Energy ............................................. 16
(1) Advancement use of thermal power generation ................................ 16
(2) Intensive use of heat, including cogeneration ................................... 18
(3) Technologies related to the next generation energy ........................... 18
(4) Stable and inexpensive securement and supply of fossil fuels , etc...... 18
4. Bold Implementation of Reform of Electricity Power Systems .......... 20
(1) Promotion of competition in the electricity market ........................... 20
(2) Neutralization and widening of the transmission and distribution sectors
........................................................................................................ 20
5. Steady Implementation of Global Warming Countermeasures.......... 22
In Undertaking the Strategy: Review and Implementation by Both the Government
and the People of Japan in Unison .............................. 24
Innovative Strategy for Energy and the Environment
September 14, 2012 The Energy and Environment Council Decision
Introduction
The Great East Japan Earthquake and the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co. (TEPCO) occurred on March 11, 2011. They posed us fundamental questions over the past we had chosen and the future we had envisaged. The value and the future of our society that we had believed in are now greatly questioned. Especially, the accident casts significant doubt on the current energy society and calls for fundamental reform.
Before the Great East Japan Earthquake, we had aimed at ensuring the stable supply of energy and sought solutions for global warming issues by increasing the dependence on nuclear energy as a pillar of our energy policy. However, by squarely looking at the somber reality that the aforementioned accident brought about and by seriously learning lessons from the accident, the Government of Japan came to firmly have believed that it would need to review from scratch Japan’s national energy strategy that it had promoted.
This new energy strategy is not a “strategy formulated only by a small number of people.” It should be a “strategy built upon national discussions held throughout Japan” where, above all, the Government of Japan and its people listen to individual views, anxieties as well as hopes with open minds, and deeply understand each other’s various opinions.
This new strategy is not a “strategy of contraction and passiveness.” It should be a “forward-looking growth strategy” that would turn constraints into impetus for dramatically diffusing and expanding energy efficiency and renewable energy with the participation of each of the people.
A strategy that is not a mere extension of the past, but leads to the creation of a new future. A strategy that is not a rash dream but is a feasible one. A strategy that is full of appreciation of and caring for local governments, where nuclear energy-related facilities are located, for having supported the development of Japan’s society and economy. Based on this firm direction, we hereby lay down an “Innovative Strategy for Energy and the Environment.”
The Innovative Strategy’s basic policy is to strive to reduce the dependence on nuclear energy as well as on fossil fuels, by maximizing green energy such as energy efficiency and renewable energy. The Strategy upholds the following three pillars, based on broad and diverse national discussions held throughout Japan.
The first pillar is the “realization of a society not dependent on nuclear power in earliest possible future.” In order to ensure its achievement, we lay down three guiding principles. We will mobilize all policy resources, particularly for the “realization of a green energy revolution,” such a level as to even enable zero operation of nuclear power plants in the 2030’s. In the meantime, the operation of nuclear power plants whose safety is assured will be restarted as an important power source.
The second pillar is the “realization of a green energy revolution.” We will establish a new framework where diverse stakeholders, including consumers, play a leading role, and vigorously advance a “Green Growth Strategy.” With the cooperation of the country, we will also promote the transformation of the current social system into the one where green energy sources will spontaneously diffuse and expand. Moreover, through these endeavors, we will firmly establish green energy as a base energy source in society, aim at enhancing the stability of energy supply and conserving the global environment, as well as encourage the emergence of a new sector for economic development.
The third pillar is the “stable supply of energy.” In order to also realize the first and second pillars, ensuring the stable supply of energy is an extremely important issue. From this perspective, we will ensure sufficient electric supply from fossil fuels, and aim at its more efficient use including the use of heat. At the same time, we will accelerate research and development of next-generation energy technology.
Moreover, we will boldly implement “reform of the electricity power systems” in order to realize the aforementioned three pillars. We will drastically reform the supply-demand structure of energy, and establish a new system where each individual plays a leading role. Specifically, we will eliminate monopolies and promote competition in the market, and separate electricity generation from transmission and distribution. We will thereby establish a network-type distributed energy system, expand the use of green energy, and realize an inexpensive and stable electricity supply.
The vigorous promotion of energy efficiency and renewable energy both at home and abroad is directly linked to steady implementation of “global warming countermeasures.” We will continuously make long-term and well planned efforts toward the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
With the “Innovative Strategy for Energy and the Environment,” the Government of Japan, together with the country, is going to build a new energy society. If the Government’s unwavering resolve and resolute undertaking of policies can be combined with the full cooperation of its people, this goal can be achieved.
Achieving this goal would mean that Japan could set a precedent to many other countries in the world and that the current generation would “fulfill its responsibility” toward the future generation.
We undertake the implementation of the “Innovative Strategy for Energy and the Environment” with determination to tackle ambitious goal that has international and historical significance.
1. Realization of a Society Not Dependent on Nuclear Power in Earliest Possible Future
Verified results of national discussions so far held throughout Japan clearly indicate that, after the experiences of an accident at TEPCO’s Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and in the ensuing sufferings of many local areas and citizens including those in Fukushima Prefecture, many people are hoping to “build a society not dependent on nuclear power”. So do those discussions, on the other hand, also reveal divergences in their views on how early it could realize and even whether it could possibly be built. Under such circumstances, it is important for the Government to show a path towards realization of a society not dependent on nuclear power.
At the same time, it is necessary to show how the Government can ensure safety of nuclear power, and how it can address the spent fuel issue, i.e., so-called backend issue, so as to overcome natural uncertainty and anxiety with nuclear power. In particular, it is necessary, taking the opportunity to select the future path, to tackle squarely the backend issue, including the nuclear fuel cycle policy issue lately brought to surface. In reflection, we have not shed enough attention for many years to the unsolved issues on means of processing and disposing spent fuels. The Government is now determined that it should not postpone but find solutions to these issues, recognizing the long history and co-operation rendered by Aomori Prefecture, and that it should call upon the whole nation, including those living in areas to enjoy consumption, to consider them seriously.
(1) Three guiding principles towards realization of a society not dependent on nuclear power
1) To strictly apply the stipulated rules regarding forty-year limitation of the operation; 2) To restart the operation of nuclear power plants once the Nuclear Regulation Authority gives safety assurance; 3) Not to plan the new and additional construction of a nuclear power plant, are the guiding principles.
In applying the three guiding principles, the Government will mobilize all possible policy resources to such a level as to even enable zero operation of nuclear power plants in the 2030’s. As its first step, the Government will compose the “Framework for Green Development Policy” by the end of this year, make it as a roadmap for the expansion of green energy, and incorporate in it goals such as the time-bound targets of saving electricity and energy conservation, targets on the amount of introduced renewable energy, technology development and dissemination, as well as the specific measures, such as budgets and regulatory reforms, which will enable these targets.
(2) Five policies towards realization of a society not dependent on nuclear power
The Government, with the Energy and Environment Council as the central vehicle, will set up new nuclear power policies which include the followings. The role of the Atomic Energy Commission will be thoroughly re-examined, through establishing a forum for re-examining the modality of it, with its abolition and reorganization in mind, while taking note of its roles such as the verification of peaceful uses of nuclear energy.
1) The nuclear fuel cycle policy
What should seriously be taken to heart, regarding the nuclear fuel cycle, is the valuable co-operation rendered by Aomori Prefecture till to date with this national policy, in shouldering roles to offer facilities for uranium enrichment, a reprocessing plant and a low-level radioactive wastes storage, and to accept temporary storage and management of wastes reprocessed abroad. In return for such co-operation, when Aomori Prefecture received spent fuel and nuclear wastes, commitments were made to Aomori Prefecture that nuclear fuel cycle policy must be promoted consistently and steadfastly in medium and long terms, that Aomori Prefecture must not become a site of final disposal of radioactive wastes, equivalent to geological disposal, and that, if reprocessing projects should be found extremely difficult to surely implement, necessary and appropriate steps be swiftly taken, which include relocation of spent fuels by Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited(JNFL) to outside its facilities. These commitments should be honored. We will keep our word strictly not to make Aomori Prefecture a site of final disposal. Also, in relations with the international community, the responsibility of nuclear non-proliferation and peaceful uses of nuclear energy should be fulfilled.
Assuming such responsibility, the Government will continue its present nuclear fuel cycle policy to engage in reprocessing projects, and will have discussions responsibly in communicating with related local governments including Aomori Prefecture and with the international community.
The following steps should be given priorities for the time being;
Research on direct disposal is to be launched.
Regarding Monju, under international cooperation, research for compiling the outcomes of the development of a fast-breeder reactor, as well as that on the reduction of the amount and toxic level of radioactive waste and other related purposes will be conducted. A research plan for a certain period of time for those purposes will be developed, implemented, and, after confirming its outcomes, completed.
Research and development of spent fuel processing technology, advanced burner reactors and others for the reduction of the amount and toxic level of radioactive wastes will be promoted.
The Government will take responsibility for the project on the backend, not simply relying on efforts made by the private sector.
The Government will establish a forum for consultation with related local municipalities and/or areas of electricity consumption and will immediately embark on works to find solutions for issues regarding direct disposal of spent fuels, those regarding institutions and means of intermediate storage, and those regarding ways to find sites for final disposal.
2) Maintaining and strengthening human resources and technology
Securing nuclear safety is a matter of the highest priority, and personnel possessing advanced technology and high safety mind should be charged with a mission of achieving nuclear safety. In particular, the advancement of technology regarding decommissioning and processing of spent fuels is an essential challenge to realize a society not dependent on nuclear power. Further, the promotion of technology and the development of human resources on decontamination and others will help to accelerate the return to the homes at the earliest possible date of those people in Fukushima being evacuated as a result of the accident at TEPCO’s Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. In addition, the development of human resources and technology on nuclear power is essential for the peaceful uses of nuclear energy, demonstration experiments regarding the effects of radiation, and technical support for the safe management and decommission of nuclear power plants in emerging nations.
The Government should develop plans for maintaining and strengthening human resources and technology by the end of this year, recognizing it as its responsibility. Such plans should include ways never to lose but to make maximum use of human resources in nuclear power related organizations, such as JNFL and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). They should also include support for technology development and fundamental researches in industries, academia and other societies so as to promote the development of new human resources in the nuclear field.
3) Cooperation with the international community Japan has ratified the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons and has promoted the peaceful uses of nuclear energy under the strict safeguards system. Its nuclear power policies, including its nuclear fuel cycle policy, have been conducted through close co-operation with other countries, starting with the United States. Re-examination of its policy to realize a society not dependent on nuclear power will be made through close consultation and collaboration with international organizations and other countries. Furthermore, it is the responsibility of Japan to contribute to strengthening nuclear safety worldwide by sharing with the world its experience and lessons derived from the nuclear accident of last year, and to offer its nuclear technologies of the highest standard in safety in the world to those foreign countries which wish to utilize nuclear technologies of our country, taking into account the situation and will of those countries.
4) Strengthening measures for local areas with nuclear power facilities
Priorities should be given to measures to be taken for those local areas which receive new requests from the Government on nuclear related facilities in them, giving sufficient care for the influences they bear. Various measures, including support for the introduction of green energy, should also be taken preferentially and intensively for those local municipalities which have nuclear related facilities
to help them to pursue structural reforms.
In addition, the Government will bear responsibility to undertake measures on the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, decontamination of Fukushima and other prefectures, and healthcare of the people of Fukushima.
5) Systems of nuclear power projects and the liability system for nuclear related damages
The systems of nuclear power projects in Japan, which have hitherto been managed and promoted by the private sector under the policy of the Government, needs to be reviewed so as to make clearer the responsibilities of both the private sector and the Government.
Necessary examination should be made regarding the future liability system for nuclear related damages, based upon the consequences of the review of the aforementioned systems, and taking into consideration the implementation of the compensation relating to the accident at the TEPCO’s Fukushima Nuclear Power Stations.
(3) Review of the path towards a society not dependent on nuclear power
The path towards the realization of a society not dependent on nuclear power should be a long way, and not a straight way. As energy mix of Japan has changed according to international energy situations and technology development trends, it is extremely difficult, at this juncture, to foresee the exact future trends. In establishing an energy strategy, we always have to be mindful of this difficulty so that any strategy should be developed to be sufficiently flexible and responsive to any unforeseen changes in the future.
Consequently, in making a path towards realization of a society not dependent on nuclear power realistic, the Government should carefully review such factors as the state of the expansion of green energy, the impact on people’s lives and economic activities, the international situation regarding energy, the level of people’s confidence in nuclear energy and the Government’s supervision, the status of cooperation and understanding of local governments on the disposal of spent fuels, and the relationship with the international community, and should constantly re-examine its nuclear policies, incessantly disclosing related information.
2. Realization of Green Energy Revolution
Innovation which should be called the green energy revolution had already started on a global basis before accident at TEPCO’s Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. In Japan, smart energy saving by utilizing IT (information and telecommunications technology) and storage batteries is entering the stage of actual use, and introduction of renewable energy is also accelerating. Although there are still economic and institutional problems such as high cost, instability, insufficient infrastructure, and various regulations at this time, Japan will push forward the green energy revolution with the clear intention of overcoming those problems through technological innovation and inductive policies and making green energy the major power source.
If the green energy revolution accelerates, breakaway from dependence on nuclear power can be moved forward. At the same time, this will produce new industries over a wide -range of regions, leading to revitalization of local areas, and, enhance energy security, and will also be effective in terms of global warming countermeasures. This change is not the mere replacement of nuclear energy with energy saving and renewable energy. It is the establishment of a new mechanism in which individual citizens change themselves from passive electricity consumers to distributed power plants or those who take a leading part in smart energy saving, according to their roles. If photovoltaic power generation, storage batteries, and fuel cells become widespread at home and in communities as ordinary items, citizens may gain income by selling electricity instead of paying electricity bills. All citizens' playing a leading part in bringing about a social change in the same manner as during the IT Revolution in the last half of the 1990s is the essence of the green energy revolution.
(1) Electricity saving and energy saving
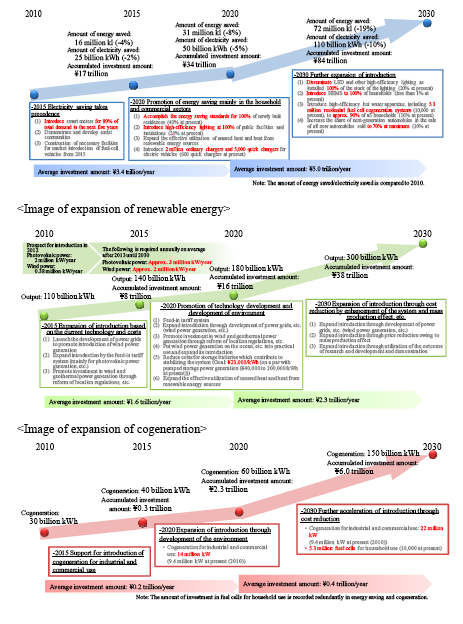
・ Regarding electricity saving, reduction of over 110 billion kWh1 compared to 2010 (1.1 trillion kWh) will be realized by 2030. In doing so, the peak demand (kW) will be significantly restrained by smart meters, HEMS/BEMS, demand response, etc.
1 This is a value on the premise of the prudent case set by the secretariat with regard to macroeconomic conditions (real economic growth rate: 1.1% in the 2010s; 0.8% in the 2020s). On the premise of the growth strategy case set by the secretariat with regard to macroeconomic conditions (real economic growth rate: 1.8% in the 2010s; 1.2% in the 2020s), the amount of reduction is 10 billion kWh. If the growth rate is high, demand for electricity and energy grows; therefore, the amount of electricity saving and the amount of energy reduction compared to 2010 are smaller.
・ Regarding energy saving, reduction of over 72 million kl2 compared to 2010 (approximately 390 million kl) will be realized by 2030 on a final energy consumption basis.
<Image of the process toward realizing the aforementioned targets3>
<Thorough implementation of inductive policies toward national development of smart energy saving> (Energy saving in the household and commercial sectors)
The energy saving performance of home appliances will be improved by the top runner standards, and others, and the introduction of energy saving equipment (LED and other high-efficiency lighting, high-efficiency air-conditioning, etc.) will be accelerated through dissemination, education, etc. In particular, efforts will be made with the aim of disseminating LED and other high-efficiency lighting to 100% of public facilities and institutions by 2020 and 100% of stock of the lighting by 2030.
The improvement of efficiency of hot water apparatus and residential fuel cell cogeneration systems will be promoted, and measures to promote their introduction will be strengthened. In particular, residential fuel cell cogeneration systems are important for households to become distributed power plants. Therefore, introduction of 1.4 million fuel cells and 5.3 million fuel cells (10 thousand fuel cells as of 2010) will be aimed at as of 2020 and 2030, respectively.
2 This is a value based on the premise of the prudent case. Based on the premise of the growth strategy case, the amount of reduction is 46 million kl. 3 These are values based on the premise of the prudent case. Based on the premise of the growth strategy case, values are as follows.
(Energy saving in the industrial sector)
・ In the industrial sector, introduction of cutting-edge technology at the time of replacement of facilities will also be promoted, and technological innovation in manufacturing processes, etc., will be aimed at.
(Energy saving in residences and buildings)
・ Regarding residences and buildings, conformity to the energy saving standards will be made obligatory in stages for all newly built residences and buildings by 2020, sufficiently taking into account the necessity, degree, balance etc. of regulations. In addition, utilization of high-performance heat insulating materials, windows, coatings, etc. will be promoted. Furthermore, introduction of the top runner standards, etc. will be aimed at through early enactment of the revised Act on the Rational Use of Energy. Regarding existing residences and buildings, energy saving renovation will be promoted.
(Energy saving by improving the efficiency of heat utilization)
Efficient utilization of urban exhaust heat (exhaust heat from factories, waste disposal factories, power plants, etc.) will be promoted, and facilitation of procedures, including that development of heat networks, will be carried forward.
Utilization of renewable heat sources ( geothermal, solar heat, heat energy from river water, sewage, snow and ice, biomass, etc.) will be expanded. (Next-generation automobiles)
・ Efforts will be made with the aim of increasing the share of next-generation automobiles in the sales of all new automobiles to 50% by 2020. Regarding fuel-cell vehicles, construction of necessary facilities for market introduction of fuel-cell vehicles from 2015 will be promoted.
(Smart electricity saving)
・ The national development of smart electricity saving (demand response) will be promoted by carrying forward installation of smart meters and introduction of HEMS/BEMS and by utilizing market mechanisms, such as a fee at peak hour, point system, and negawatt trade, in addition to visualization of electricity saving.
(Energy saving in communities and in urban areas, such as smart communities.)
・ In order to expand mechanisms like the aforementioned smart electricity
saving to communities and urban areas, dissemination of smart houses and realization of smart communities will be carried forward by utilizing the outcome of the smart community demonstration projects, etc. In addition, shift to compact cities, etc. will be promoted through consolidation of urban functions in collaboration with promotion of utilization of public transportation, etc. by utilizing the Act on Promotion of Low Carbon City, and others
(Explanation of burden, and others)
・ The fact that sharing of costs for certain equipment investment and changes of consumption behaviors are prerequisites for realizing the aforementioned goals will be explained to all citizens through careful information disclosure.
(2) Renewable energy
・ Regarding renewable energy,4 development of over 300 billion kWh by 2030 from 110 billion kWh in 2010 (three times) will be realized [if hydroelectric power is excluded, from 25 billion kWh in 2010 to 190 billion kWh (eight times) by 2030].
<Image of the process toward realizing the aforementioned targets>
<Mass introduction of renewable energy> (Induction of private investment by the feed-in tariff system)
・ Mass production effect will be realized while further promoting investments by various actors through effective operation of the feed-in tariff system. (Public investment in public facilities, etc.)
4 "Renewable energy" originally does not include waste power generation. However, here, "renewable energy" includes waste power generation for convenience sake.
・ Installation of photovoltaic power generating equipment, storage batteries, etc. will be promoted at public facilities, etc. Regarding biomass power generation, introduction of high-efficiency power generating equipment at waste incineration facilities and introduction of biomass power generating equipment at wastewater treatment plants will be carried forward. In addition, efforts will be made to utilize those facilities as local energy centers which supply energy at the time of disaster.
(Community-led acceleration of introduction)
・ Support will be provided for the community-led acceleration of introduction of renewable energy taking into account the characteristics of the communities. In doing so, improvement of energy infrastructure and community building will be carried forward in an integrated fashion.
(Reform of land use regulations and simplification and speed-up of environmental impact assessment procedures)
・ Constraints that inhibit introduction of renewable energy will be removed through reform of various land use regulations, simplification and speed-up of the procedures based on the Environmental Impact Assessment Act for the purpose of accelerating expansion of wind and geothermal power generation, and solution of problems in connecting with a grid system.
(Transmission System Reinforcement including construction of wind power grid)
・ Transmission System Reinforcement including construction of wind power grid will be taken, including starting development of power grids for promoting introduction of wind power generation.
(Transmission system stabilization)
・ In response to expansion of introduction unstable renewable of power sources, such as solar and wind power, transmission system stabilization measures will be taken, including securing of thermal power generation mentioned in Section 3, extensive operation of power grids mentioned in Section 4, and development of an environment for promoting introduction of large-scale storage batteries.
(Renewable heat)
・ Utilization of renewable heat sources (geothermal, solar heat, heat energy from river water, sewage, snow and ice, biomass, etc.) will be expanded. [already mentioned]
(Research and development and demonstration)
・ Efforts will be made to put power generation utilizing ocean energy sources, such as wave and tidal power, into practical use in the medium and long term while accelerating technology development and demonstration experiments relating to high-efficiency photovoltaic power generation, offshore wind power generation,, high-density storage batteries, advanced geothermal development, and high-efficiency biomass power generation, including the development of related materials and parts.
(Explanation of burden, etc.)
・ The fact that sharing of charges under the feed-in tariff system and costs for system strengthening measures and system stabilization measures is a prerequisite for realizing the aforementioned targets will be explained to all citizens through careful information disclosure.
In light of the content mentioned above, the government will formulate the "Framework for Green Development Policy," which put the process toward realizing the green energy revolution into concrete form, by around the end of this year through the meetings of the Energy and Environment Council, and will share the targets and burdens by presenting the Framework to citizens.
3. For Ensuring Stable Supply of Energy
It was also confirmed through national discussions held throughout Japan that many people and companies have concern and anxiety, that is, " would people's living and industry truly be all right should there be no more nuclear power plants?". The conventional energy policy set the realization of "three Es" (energy security (securing of stable energy supply), environment (environmental friendliness), and economic efficiency (economic efficiency by utilizing market functions in sufficient consideration of the former two Es)) as its goal. Although it is natural to give top priority to the pursuit of safety in this Strategy as the absolute premise, these "three Es," in particular, stable energy supply at low price, remain important. In the analysis of economic impact of the options presented before, a certain impact is estimated for every scenario. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the impact on the Japanese economy and people's living as well as to promote reduction of burden and smooth conversion of the industrial structure for SMEs and industries that are especially significantly affected.
It was revealed that, different from the conventional perception, costs for nuclear power are not comparatively low, if social costs are included and that nuclear e power also has a problem in terms of stable supply as a large-scale concentrated power source. Moreover, at this moment, most renewable energy sources are high cost and their supply is unstable in many cases. Under such circumstances, thermal power generation will become increasingly important at least for the immediate future. On the other hand, if efforts are made to expand green energy, and others, and their expansion is realized, the amount of fossil fuels consumed will be smaller than now.
Regarding thermal power generation, though it has a problem in terms of global warming countermeasures, Japan has advanced environmental technology unique in the world. Thus, a strategy that links such technology to Japan’s contribution to the rest of the world and to its export and growth is also necessary. Moreover, in light of the international energy situation, it is necessary to pay sufficient attention to the fact that stable and inexpensive procurement of fossil fuels is a serious issue that affects the Japanese economy and society.
(1) Advancement use of thermal power generation
(LNG thermal power generation)
・ Regarding LNG thermal power generation, which has relatively lower CO2 emissions compared to other types of thermal power generation and which is
expected to perform a high adjustability function at the time of dissemination of renewable energy, domestic pipelines will be developed and the route of import from North America, etc. will be established, thereby realizing a stable and inexpensive supply of natural gas, the fuel of LNG thermal power generation. Moreover, conversion to high-efficiency combined cycle plants will be carried forward. In addition, technology development toward further increasing efficiency will be promoted.
(Coal thermal power generation)
・ Coal thermal power generation will play a more important role as the base power source in carrying forward reduction of dependence on nuclear power. In addition, as its introduction overseas is expected to advance. Japan's technology for coal thermal power generation that has high environmental performance will be expanded overseas. As a result, Japan will carry forward international contribution in terms of global warming countermeasures.
(Appropriate power source composition)
・ Introduction of the latest facilities through replacement of old thermal power generating equipment and establishment of new and additional coal and LNG thermal power plants will be promoted in order to realize a balanced power source composition of coal, LNG, and oil thermal power generation, comprehensively taking into account fuel characteristics, stability of supply, environmental burden, costs, adjustability function at the time of dissemination of renewable energy, etc.
(Environmental impact assessment)
・ Regarding replacement of highly-aged thermal power generating equipment with the latest facilities, reduction of environmental burden is aimed at in many cases. Therefore, efforts will be made to simplify and speed up environmental impact assessment, with the aim of shortening the assessment period of, which required around three years in the past, to a little over one year at the shortest in the case where cooperation from municipalities and business operators can be obtained. Moreover, in parallel, efforts will be made to speed up environmental impact assessment regarding new and additional installations of the latest facilities for coal and natural gas thermal power generation which are highly efficient and have small CO2 emissions.
(2) Intensive use of heat, including cogeneration
・ Effective utilization of energy will be promoted through dissemination of cogeneration (combined heat and power), including fuel cells, to the maximum extent. For this purpose, an environment that enables smooth selling of electricity from cogeneration will be developed, and measures to support introduction of cogeneration facilities will be strengthened.
<Image of expansion of cogeneration>
・ Utilization of heat from renewable energy sources ( geothermal, solar heat, river heat, sewage heat, snow and ice heat, biomass heat, etc.) will be expanded. [already mentioned]
・ Efficient utilization of urban exhaust heat (exhaust heat from factories, waste disposal factories, power plants, etc.) will be promoted, and facilitation of procedures, including that of the development of heat pipe networks, will be carried forward. [already mentioned]
(3) Technologies related to the next generation energy
・ Research and development toward putting next-generation energy networks, such as hydrogen networks, and technologies related to the next generation energy, such as CCS (carbon dioxide capture and storage), into practical use will be promoted in addition to research and development in the fields of unused energy sources, such as methane hydrate.
(4) Stable and inexpensive securement and supply of fossil fuels , etc.
・ In light of the "Strategy for Securing Natural Resources,"5 efforts will be made to secure stable and inexpensive oil, natural gas, coal, etc. through establishment
5 Reported at the Ministerial Meeting on Deployment of Integrated Infrastructure Systems on June 27, 2012.
and strengthening of comprehensive and mutually-beneficial bilateral relationships with resource-rich countries, strengthening of support for Japanese companies' acquiring upstream interests, stabilization of the market, promotion of efforts to strengthen procurement and bargaining power, etc.
Based on the "Ocean Energy and Mineral Resource Development Plan,"6 efforts will be made to strengthen the development of ocean energy and mineral resources, including oil, natural gas, and methane hydrate, in Japan.
Supply infrastructure designed to support the shift to natural gas in the future, including domestic pipelines, will be developed.
Stockpiling of oil and LP gas, which is the last resort of ensuring of energy security, and maintenance and strengthening of supply chains will be steadily promoted taking into consideration measures against disasters.
6 Approved at the meeting of the Headquarters for Ocean Policy on March 24, 2009.
4. Bold Implementation of Reform of Electricity Power Systems
In order to realize the three pillars, "realization of a society not dependent on nuclear power in earliest possible future" "realization of a green energy revolution," and " ensuring stable supply of energy," it is necessary to drastically reform the mechanism concerning energy. Up till now, it had been possible to provide in advance a power source composition ratio considered to be the "best mixture" through substantive agreement between the government and electric power companies. However, in the future, the results of the entry of various suppliers into businesses such as renewable energy power generation, and those of participation in energy saving by countless numbers of consumers by their own choices will decide the actual power source composition. Networks available for everyone and a competitive market are indispensable for a mechanism in which citizens play a major role. The "reform of electricity power systems" is a measure to establish such a distributed network system.
(1) Promotion of competition in the electricity market
- Freedom of "choice of electricity" will be guaranteed for all citizens through full liberalization of the retail market, and introduction of related services, including demand response, will be promoted.
- Competition in power generation and the retail market will be promoted through abolition of regulations for wholesale and vitalization of the wholesale market, thereby aiming at cost reduction and enrichment of customer services.
(2) Neutralization and widening of the transmission and distribution sectors
The generation sector and the transmission and distribution sectors will be separated functionally or legally. Hereby, power grids will be opened up to all business operators, including those engaged in the business relating to renewable energy and cogeneration, in a neutral and equitable manner.
A neutral organization that operates the system across regions will be established, thereby realizing extensive operation of power grids. Hereby, the instability of renewable energy will be alleviated, and conversion to a mechanism that effectively utilizes supply capacity in an extensive manner will be realized.
Enhancement of inter-regional and intra-regional power-grids will be carried forward in order to effectively utilize extensive supply capacity including renewable energy, and vitalize the market.to achieve the goal, In doing so, the government will provide policy support as needed while making investment recovery by the private sector through the collection of network usage charges, etc. a principle.
The government will formulate the "Strategy for Reform of Electricity Power Systems (tentative name)”, which gives shape to the content mentioned above, by around the end of this year and present it to citizens.
5. Steady Implementation of Global Warming Countermeasures
Prevention of global warming is the common challenge of humankind. The discussions toward establishment of a post-2020 future framework applicable to all parties are underway in aiming at achievement of the ultimate objective of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change7. In this zero-based re-examination of energy policy, there is no change in Japan’s stance to work toward achievement of the ultimate objective of the Convention.
Japan has decided that it will aim at 80% reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 in its Fourth Basic Environment Plan (Cabinet decision on 27 April 2012), and Japan will take necessary measures in a long-term and well-planned manner.
In addition to the large-scale introduction of renewable energy and nationwide promotion of energy efficiency as mentioned above, Japan will implement drastic measures on greenhouse gases other than CO2 from energy sources, such as HFCs or PFCs with high global warming potential, in a cooperative manner between the Government and people. In these ways, Japan aims to reduce about 20% of greenhouse gas emissions domestically in 2030 compared to 19908.
The domestic greenhouse gas emissions in Japan as of 2020 needs some latitude due to uncertainty over the nuclear power reactors’ operation. The emissions as of 2020 could be calculated 5-9%9 reduction compared to 1990 with a certain assumption10
In addition to these domestic efforts, Japan will actively promote measures on forest as well as other carbon sinks and international cooperative reduction efforts.
Japan aims at ensuring 3.5% removal amount by forest sinks on average from
7 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change establishes that its objective is “stabilization of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system”
8 This is premised on the prudent case. If it is based on a growth case, the reduction will be about 10% (compared to 1990 levels).
9 The dependence level of nuclear power in 2020 is calculated as the rough midpoint of the line between the levels of 2030 and 2010.
10 This is premised on the prudent case. If it is based on the growth strategy case, the reduction will be 2-5% (compared to 1990 levels).
2013 to 2020 as the allowed cap (about 3% as of 2020) through adequate forest management and timber use promotion. Moreover, Japan will also produce seedlings of fast-growing varieties and enhancing forest resources appropriately in order to remain forest sinks removal beyond 2020.
Japan has environmental technologies such as highly efficient coal-fired power generation technology. The efforts including the diffusion of these technologies overseas will contribute to a significant reduction of global greenhouse gases emissions. Japan promotes global reduction of greenhouse gases emissions by the use of mechanisms including the Bilateral Offset Credit Mechanism and Joint Crediting Mechanism where emissions reductions in recipient countries through the use of Japan’s technologies and others can be counted as a part of reductions towards achieving Japan’s reduction target, and these approaches will be a main pillar of Japan’s international contribution.
Japan will formulate overall government efforts as an “Adaptation Plan” with the view to reacting (adaptation) to the unavoidable impact of climate change.
Taking into account the contents mentioned above, the Government will formulate its “Global Warming Action Plan” for the period from 2013 by the end of this year for presentation to its people and the international community.
In Undertaking the Strategy: Review and Implementation by Both the Government and the People of Japan in Unison
For the successful implementation of the “Innovative Strategy for Energy and the Environment,” it is indispensable to assemble the forces of all the nation. The Government of Japan is determined to make a policy change in a responsible manner so that all the people will be able to take part in the creation of this new energy society. In order to make the path toward a society not dependent on nuclear power realistic, the Government will review and constantly re-examine the Strategy such factors as the state of the expansion of green energy, the impact on people’s lives and economic activities, the international situation regarding energy and the environment, the level of people’s confidence in nuclear energy and the Government’s supervision, the status of cooperation and understanding of local governments on the disposal of spent fuels, and the relationship with the international community.
In doing so, the Government will disclose information to the people of Japan and the international community in a detailed manner through a process that will sufficiently ensure transparency. An organizational structure necessary to review the Strategy will be established within the Cabinet Secretariat.
From the era when the Government and electric power companies developed large-scale electricity sources and single-handedly provided electricity upon demand from the people, toward the era when each of the people will choose, create and store necessary energy by herself/himself. This transformation of the social system cannot be easily realized. However, we firmly believe that we will be able to achieve this transformation if the Government lays out a vision for this transformation, upholds ambitious policies, and makes all-out efforts to minimize burdens ensuing from this policy change on people’s lives as well as the economy and industry.
The “Innovative Strategy for Energy and the Environment” is a map that leads us to the future, indicating the way we should move forward.
(Exhibit) <Image of expansion of energy saving>